Please select root levels for the menu
NZ Plants
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction introduces genetic variability into a population and results in an embryo that grows into a sporophyte plant. Moss life cycle
Male and female structures
In many mosses, antheridia (sperm-forming structures) and archegonia (egg-containing structures) are in groups and encircled by leaves at the tips of stems. In some mosses, both antheridia and archegonia are on the same plant, but in other mosses they are on separate plants.
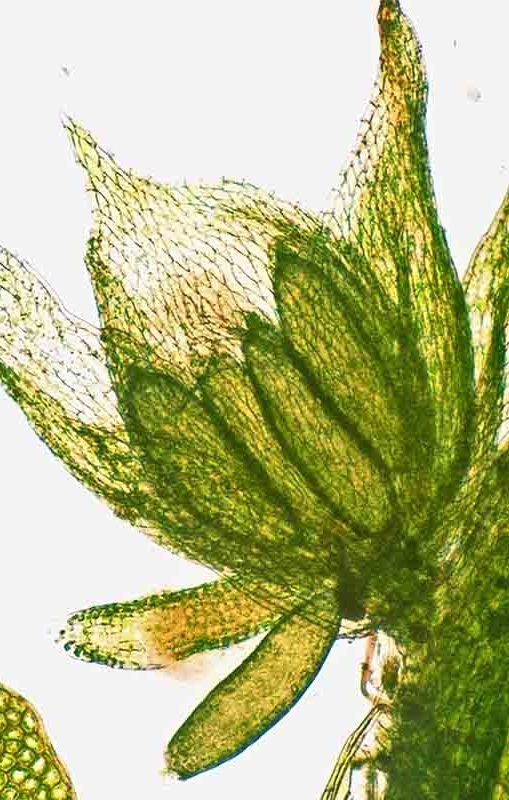

Calyptrochaeta brownii - Broad leaves (pale green) encircle a group of smaller, sausage-shaped antheridia (deep green) at the tip of a male stem. Each antheridium produces numerous biflagellate sperm cells.
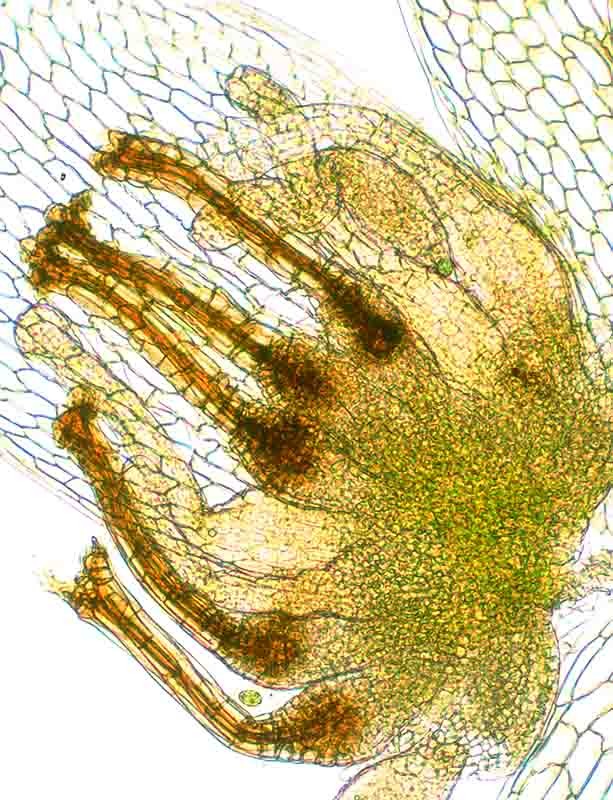
Distichophyllum pulchellum - A cluster of archegonia forms at the tip of a female stem. Each archegonium consists of an enlarged egg-containing basal portion (the venter) and a long neck with a central canal. Sperm are guided down the canal to reach the egg.
Carrying the sperm to the female
In many mosses the leaves around the male stem tip that encircle the antheridia form a 'splash cup'. Sperm are released into rainwater or condensation that collects within the cup and are then splashed out when rain drops strike the water. In this way the sperm are carried to the archegonia on nearby plants.

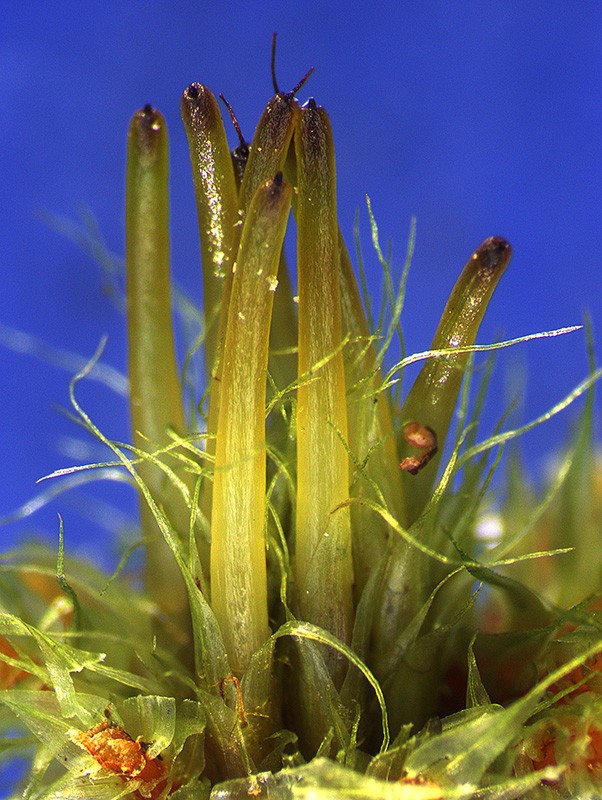
Campylopus pallidus - A male stem tip with a splash cup containing numerous sausage-shaped antheridia.
See Find by Genus page for more on Campylopus species

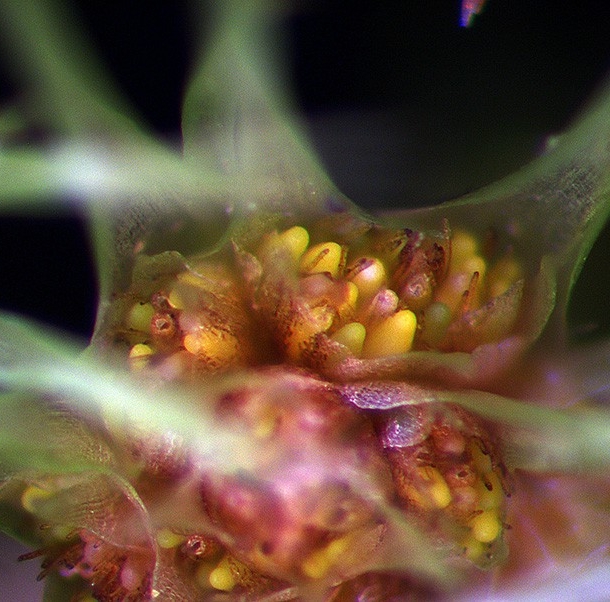
Mniodendron comatum - A female stem tip has small archegonia contained within perichaetial bracts. These archegonia have been fertilised and have enlarged so that they extend beyond the basal perichaetial bracts.
See Find by Genus page for more on Mniodendron species.
Dwarf male plants
In a few mosses if a spore lands on the leaf of a female plant it germinates to form a greatly reduced male plant. These are often referred to as 'dwarf males' because they are so much smaller than the female moss plant.
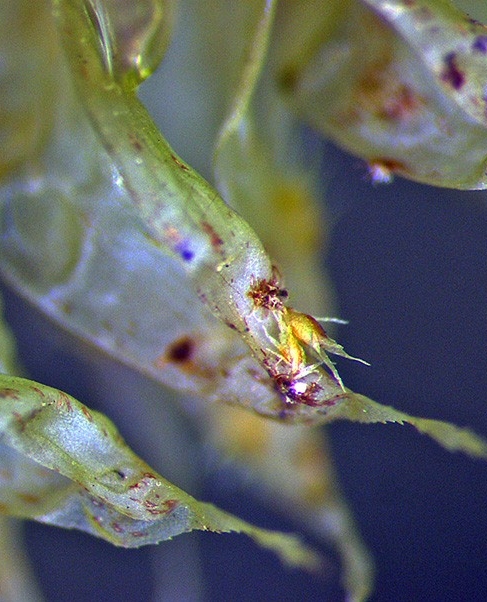

Ptychomnion aciculare - A portion of a leaf with an attached dwarf male plant.
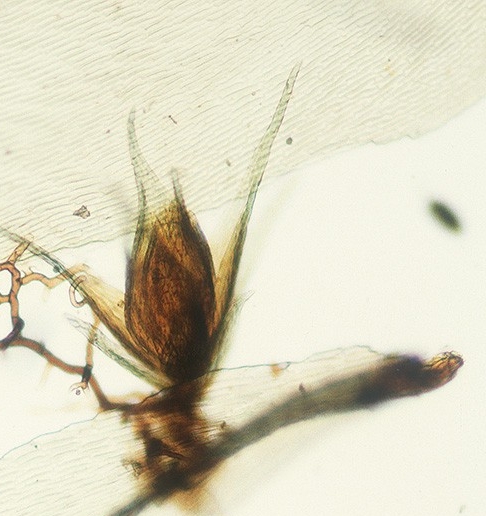

Ptychomnion aciculare - A detached portion of a leaf with an attached dwarf male.

